 Jean-françois Berthet - Jul 5, 2025
Jean-françois Berthet - Jul 5, 2025Comparison: Flutter vs .NET MAUI

Introduction
In recent years, the rise of cross-platform frameworks has profoundly transformed mobile development strategies. Companies seek to reduce costs, share skills, and accelerate delivery cycles, while maintaining high standards for quality, performance, and user experience.
In this context, two approaches stand out:
- Flutter, backed by Google, based on Dart, with a declarative UI approach and a proprietary rendering engine.
- .NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI), evolution of Xamarin by Microsoft, integrated into the .NET and C# ecosystem.
This article offers an in-depth comparative analysis of these two solutions, aimed at tech leads and mobile developers facing architectural or stack choices in their projects.
The goal is to clearly identify the strengths, weaknesses, and preferred use cases of each technology, through a set of key criteria: productivity, performance, native integration, maintainability, ecosystem, and more.
Note : we chose not to include React Native in this comparison, to focus the analysis on two contrasting but emerging approaches in different technological contexts. React Native will be the subject of a dedicated article, allowing for a broader evaluation later.
Whether you are in the scoping phase, redesigning a mobile app, or seeking a unified technical foundation across platforms, this comparison aims to provide you with an objective and directly usable framework for making the right decisions.
General presentation of the Frameworks
Before diving into the detailed comparative analysis, it is essential to lay the groundwork by presenting the two frameworks on fundamental aspects: publisher, main language, year of creation, target platforms, technical approach, and some reference application examples.
These generalities help to better understand the DNA of each technology, their strategic positioning , and the ecosystems in which they fit. They also provide a first level of insight to anticipate possible affinities with a team's skills or a project's constraints.
.NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI)
- Created by : Microsoft
- Language : C# (and XAML for UI)
- Year of creation:Stable versionMay 23, 2022 (with .NET 6), Major improvements : with .NET 7 (November 2022) and .NET 8 (November 2023)
- Target : Android, iOS, macOS, Windows
- Approach : Wrapper over native controls with a shared codebase
- Reference applications : NBC Sports, Bitwarden, Azure Mobile app, SportsEngine, Microsoft 365 Admin
Flutter
- Created by : Google
- Language : Dart
- Year of creation:Stable version 1.0 : December 4, 2018, Flutter 2.0 (web and desktop beta support): March 3, 2021,Flutter 3.0 (stable support for Android, iOS, Web, macOS, Windows, Linux): May 11, 2022 (Google I/O)
- Target : Android, iOS, Web, Desktop (Windows, macOS, Linux)
- Approach : Custom rendering (Skia) with native-like widgets
- Reference applications : Google Pay, Alibaba, eBay, Reflectly, SNCF Connect
.NET MAUI (Multi-platform App UI)

The .NET (.NET MAUI) cross-platform application user interface is a cross-platform infrastructure for building native mobile and desktop applications with C# and XAML. It is the successor to Xamarin.Forms, integrated into the .NET 6+ ecosystem.
With .NET MAUI, you can develop applications that run on Android, iOS, macOS, and Windows from a single shared codebase.
General Architecture
- Language : C# (with XAML or code-behind)
- Strongly typed, object-oriented language.
- Uses .NET 6/7/8+with the MAUI SDK.
- UI via XAML (similar to WPF/UWP) or in C# fluent code.
- MAUI Structure :
- Shared UI (.xaml or .cs)
- Shared back-end (C#, services, models)
- Handlers : abstractions to access native controls.
- Blazor Hybrid : allows using Razor/HTML/CSS for the interface.
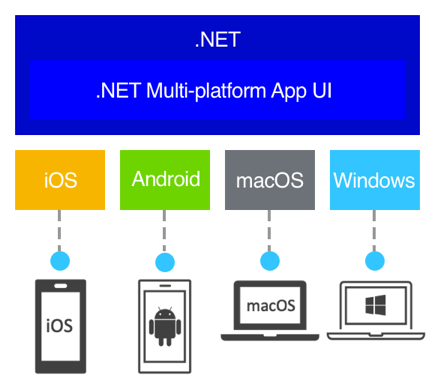
.NET MAUI is intended for developers who want to:
- Write cross-platform applications in XAML and C#, from a single shared codebase in Visual Studio.
- Share UI layout and design across multiple platforms.
- Share code, tests, and business logic across multiple platforms.
Development Environment
- MAUI CLI (`dotnet new maui`, `dotnet build`, etc.)
- Hot Reload (XAML/C#)
- Debugger, Live Preview, XAML Live Visual Tree
- Integrated device simulators (Android/iOS)
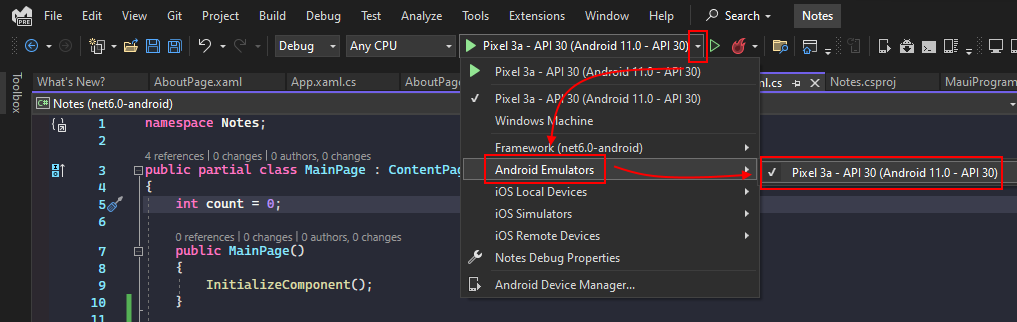
Android Emulator
The Android emulator is directly integrated into Visual Studio and simulates an Android device on your computer. It allows you to launch, test, and debug applications without using a real physical device.
Android SDK, Android Emulator, AVD Manager (included with Visual Studio when you install MAUI for Android).
UI Development
- UI in XAML (declarative, similar to WPF)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8" ?> <ContentPage xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/dotnet/2021/maui" xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2009/xaml" x:Class="Notes.AboutPage"> <VerticalStackLayout Spacing="10" Margin="10"> <HorizontalStackLayout Spacing="10"> <Image Source="dotnet_bot.png" SemanticProperties.Description="The dot net bot waving hello!" HeightRequest="64" /> <Label FontSize="22" FontAttributes="Bold" Text="Notes" VerticalOptions="End" /> <Label FontSize="22" Text="v1.0" VerticalOptions="End" /> </HorizontalStackLayout> <Label Text="This app is written in XAML and C# with .NET MAUI." /> <Button Text="Learn more..." Clicked="LearnMore_Clicked" /> </VerticalStackLayout> </ContentPage> - And in C#
private async void LearnMore_Clicked(object sender, EventArgs e) { // Navigate to the specified URL in the system browser. await Launcher.Default.OpenAsync("https://aka.ms/maui"); }
State Management and Logic
- Recommended MVVM (Model-View-ViewModel) pattern
- Use of `INotifyPropertyChanged`, `Command`, etc.
- Compatible with `CommunityToolkit.Mvvm`
There are three main components in the MVVM model: the model, the view, and the view model. Each serves a distinct purpose. The diagram below shows the relationships between the three components.
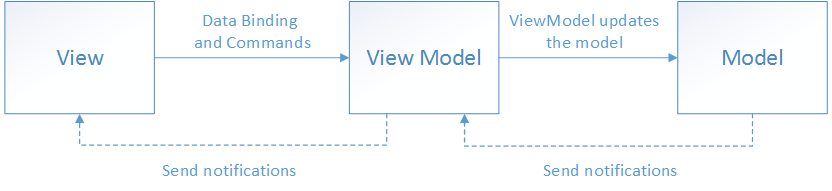
At a higher level, the view "knows" the view model, and the view model "knows" the model, but the model is unaware of the view model and the view model is unaware of the view. Thus, the view model isolates the view from the model and allows the model to evolve independently of the view.
Navigation
- Via `Shell` (`AppShell.xaml`) for centralized navigation
- `Routing.RegisterRoute()` and `GoToAsync()`
API Calls and Persistence
- HTTP via `HttpClient`
- JSON serialization with `System.Text.Json` or `Newtonsoft.Json`
- Storage:
- `Preferences` (key/value)
- `SecureStorage` (encryption)
- SQLite (via `sqlite-net-pcl`)
- EF Core (with SQLite for mobile)
Tests
- Unit tests: `xUnit`, `NUnit`
- UI tests: with `MAUI.UITest` (preview) or Appium
- Mock : `Moq`, `FakeItEasy`
Build & Deployment
- Visual Studio offers build for each platform
- `dotnet publish` / `dotnet build`
- Integration with Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions, CI/CD
- Deployment to Play Store / App Store / Microsoft Store
Publishing possible directly from Visual Studio…
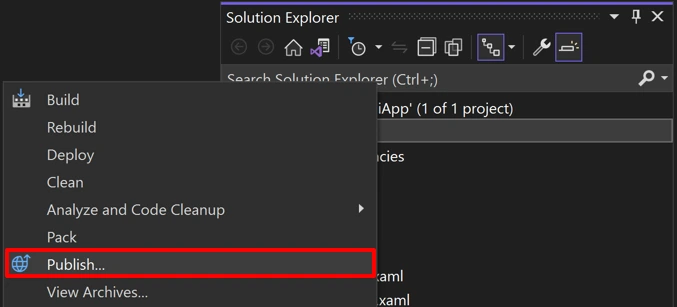
Creation and signing of the package for distribution
.NET MAUI allows you to generate:
- APK (old format) or
- AAB (Android App Bundle) (format recommended by Google).
Documentation
Flutter

Flutter is an open-source UI framework developed by Google for creating native multi-platform applications with a single codebase. It uses the Dart language and offers custom graphics rendering via its own engine.
General Architecture
- Language: Dart
- Object-oriented language, compiled to native code (JIT & AOT).
- Syntax similar to JavaScript and Java/C#.
- Package manager: pub.dev.
- Key components:
- Widgets : Everything is a widget (UI, layout, animation, etc.).
- State Management : Several solutions:
- setState (basic)
- Provider, Riverpod, Bloc, Cubit, GetX, etc.
- Flutter Engine : C++ engine rendering via Skia.
- Platform Channels : Allows calling native code (Kotlin, Swift, etc.).
Development Environment
- Recommended IDEs:
- Android Studio
- Visual Studio Code
- IntelliJ IDEA
- Tools:
- Flutter CLI (`flutter doctor`, `flutter build`, `flutter run`, etc.)
- Hot Reload: instantly updates the UI without restarting the app.
- Dart DevTools: debugging, performance, logs, widget inspector.
UI Development
Flutter enables pixel-perfect design , with many capabilities:
MaterialApp,Scaffold,AppBar,Container,Row,Column,Stack- Highly composable custom components
- Responsive design with
LayoutBuilder,MediaQuery,Flexible
State Management
Depending on your project's complexity:
- Simple →
setState - Medium →
ProviderorRiverpod - Complex →
Bloc,Cubit,Clean Architecture
Navigation
- Native (
Navigator,Navigator 2.0) - With packages like:
go_routerauto_route
API Calls and Persistence
- HTTP:
http,dio,chopper - Local storage:
shared_preferences(key-value)sqflite(SQLite)hive(fast NoSQL)
- Authentication : Firebase, OAuth, etc.
Firebase
Integrating Firebase into a Flutter application offers many advantages, whether for development, user management (password, recovery, email sending…), FCM notifications, or Google Analytics.
Firebase offers a set of packages maintained and optimized for Flutter (firebase_core, firebase_auth, cloud_firestore, etc.).
| Domain | Advantage |
|---|---|
| Authentication | Fast multi-provider integration |
| Data | Real-time NoSQL database |
| Notifications | Easy cross-platform push |
| Analytics | User behavior insights |
| Storage | Secure file management |
| Performance | Crashlytics, Remote Config, App Check |
| Deployment | App Distribution and CI/CD support |
Tests
flutter testfor unit testsflutter_driverorintegration_testfor integration testsmockito,bloc_testfor mocking and logic verification
Build & Deployment
flutter build apk/flutter build ios/flutter build web- Integration with GitLab CI/CD, GitHub Actions, Codemagic, etc.
- Use of Flavors for multi-environment dev/uat/prod management
flutter run --flavor dev
Documentation
Framework Comparison
After setting the general framework, let's get to the heart of the comparison . We analyzed Flutter and .NET MAUI according to the most decisive technical criteria for mobile development teams: portability, performance, UX, productivity, backend integration, and learning curve.
Each strength is put into perspective with the structural or contextual limitations specific to each framework: language, maturity, native experience, or testing and deployment constraints.
The goal : to provide a clear and pragmatic framework to guide your technology choices according to your project's specific challenges.
Advantages
| Criterion | Flutter | .NET MAUI |
|---|---|---|
| 🌍 Portability | Truly cross-platform (mobile, web, desktop) | Multi-platform but not yet for Web |
| 🧱 UI/UX | Full control thanks to the Skia rendering engine. Homogeneous UI across all platforms | Native UI (thanks to wrappers), so very "OS-specific" feel |
| 🚀 Performance | Very smooth as rendering is independent (no native bridge) | Good performance but depends on the native layer |
| 🔁 Hot Reload | Very fast and stable | Available but less responsive than Flutter's |
| 🌐 Ecosystem | Large community, wide choice of packages (pub.dev) | Integrated into the .NET ecosystem (NuGet, Azure, etc.) |
| 🧠 Learning curve | Easy to learn for front-end developers | Easy if you already know C# and .NET |
| 📦 Backend Integration | Good integration with Firebase, REST, GraphQL, etc. | Very good integration with the Microsoft ecosystem (.NET, EF, Azure, etc.) |
Disadvantages
| Criterion | Flutter | .NET MAUI |
|---|---|---|
| 🔤 Dart Language | Less popular, harder to recruit developers | C# is widely used, especially in enterprises |
| 📚 OS Documentation | Fewer native APIs exposed directly (need plugins or channels) | Native integration, but sometimes complex depending on the platform |
| 🧪 Maturity | Stable, but some platform-specific bugs | Still young (replacement for Xamarin.Forms), sometimes unstable |
| 📱 Native UI | Not "real native", may lack precise native behaviors | Based on native components, so more consistent with the OS |
| 🧩 App size | Binaries are larger (Skia embedded) | More optimized size (depending on OS) |
| 🧪 Unit testing | Less support for native UI tests | Very good support with Visual Studio tooling |
Specific Comparison
Beyond use cases and developer profiles, certain technical and ecosystem aspects can strongly influence the choice between Flutter and .NET MAUI .
This table highlights the concrete differences on key points for teams :tooling, deployment, portability, and architecture paradigms.
This comparison allows you to quickly assess the framework's compatibility with existing tools, as well as the expected learning curve based on development habits. It is especially useful for multi-platform projects or those integrated into advanced CI/CD cycles.
| Aspect | Flutter | .NET MAUI |
|---|---|---|
| Preferred IDE | VS Code, Android Studio | Visual Studio 2022+ |
| CI/CD Integration | GitHub Actions, Codemagic, GitLab CI | Azure DevOps, GitHub Actions |
| Web Support | Yes | No |
| Linux Desktop Support | Yes | Unofficial / experimental |
| Navigation / Routing | Flexibility with GoRouter, etc. | Classic XAML navigation |
| Recommended Architecture | Bloc, Provider, Riverpod | MVVM (.NET standard) |
Choice by Developer Profile
Beyond technical or functional criteria, the available developer profile and the existing ecosystem play a key role in choosing a cross-platform framework. Good alignment between internal skills and the chosen technology helps reduce ramp-up time, limit project risks, and maximize productivity from the first iterations.
The table below offers a pragmatic recommendation based on developer profile or team context, to facilitate adoption and optimize project success.
| Developer profile | Recommendation |
|---|---|
| Front-end developer | Flutter (easier to approach) |
| Experienced .NET / C# developer | .NET MAUI |
| Need Web + Mobile | Flutter |
| Project with Microsoft ecosystem (Azure, SQL Server) | .NET MAUI |
| Target Linux/Desktop | Flutter |
Concrete Use Cases
In a context where mobile and desktop applications must be delivered faster, on more platforms, and with ever higher experience quality, choosing a cross-platform development framework has become a strategic issue.
Among modern options,Flutter and.NET MAUI stand out as two solid candidates, but their philosophies, strengths, and target use cases differ significantly.
This document offers a concise overview of these differences through concrete use cases, to inform decisions based on business, technical, and organizational context.
- Flutter
- UX-first applications with rich animations
- Startups targeting multiple platforms quickly
- Cross-platform projects with a single language (backend & frontend possible in Dart)
- .NET MAUI
- Internal professional applications
- Companies already using C# / Azure
- Applications requiring deep access to native Windows / macOS APIs
Conclusion
In summary, Flutter and.NET MAUI are two powerful frameworks for cross-platform application development.
Flutter stands out for its fast development, its broad compatibility with many devices, and the support of an active community.
Conversely, .NET MAUI is particularly suited for projects that leverage the .NET ecosystem, with a familiar language (C#) and excellent integration with Microsoft tools.
The choice between the two depends primarily on the specific needs of the project, the team's skills, and the tools and technologies already in place.
| Main criterion | Best choice |
|---|---|
| Fast development | Flutter |
| Performance | Flutter |
| Native system integration | .NET MAUI |
| .NET backend required | .NET MAUI |
| Web port included | Flutter |
| Smooth learning curve for .NET devs | .NET MAUI |
| Maturity | Flutter |
| UI design and visuals | Flutter |